Iron levels of just 0.3 mg/L can change the color and taste of our drinking water. So, it’s natural to want to remove the iron from our water, and a water filter pitcher may be the ideal solution.
Water filter pitchers with activated carbon filters or ion exchange resins can effectively remove excess iron from water. Granular activated carbon (GAC) filters are particularly effective at removing ferric (insoluble) iron, while ion exchange resins can remove ferrous (soluble) iron from water.
This article will explain how iron enters the water and its negative effects. More importantly, we will detail how water filter pitchers remove iron and highlight the best water filter pitchers available for removing iron.
What is iron, and how does it enter our water?
Iron is one of the planet’s most abundant resources, making up at least 5% of the crust and an incredible 35% of the entire Earth.
Overtime water that permeates the ground and underlying geologic formations dissolves rocks and minerals, releasing iron (and other elements) allowing it to seep into our rivers and reservoirs that provide groundwater for our wells and city water supplies.
This process of iron entering our water supply is completely natural.
However, iron leaching into a domestic water supply is often caused by corrosion of old pipes.
Forms of Iron
There are three main types of iron found in water, including:
1-Organic iron
Water with organic iron is often yellow or brownish in color, but it may be colorless. Water from wells affected by iron-containing surface water or shallow wells is more likely to have organic iron.
2-Ferric Iron
The water coming from a faucet that contains ferric iron is typically red, brown or yellow in color at first glance. Ferric iron is also known as the ‘red water iron’.
3-Ferrous Iron
Water containing ferrous iron is clear at first but turns brown or red after standing for a while as some of the iron settles out at the bottom of the glass. ‘Clear-water iron’ is another name for ferrous iron.
Negative Effects of Iron
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) classes the problems caused by excess iron in water under two categories:
1. Aesthetic
The aesthetic effects of iron include an unpleasant taste and/or odor, as well as the discoloration of the water.
2. Technical
Iron can lead to serious damage of a water system or decreased treatment efficiency for other contaminants in purification systems, including reverse osmosis, under-sink and whole house systems. Corrosion-related staining (which is usually orange) and corrosion itself can permanently stain household fixtures.
The flow of water can also be reduced by corroded iron pipes.
Some specific downsides of excess iron in water include:
- Iron concentrations as low as 300 ug/L can leave reddish brown stains on clothes, tableware, and pipework that are very difficult to remove. The iron particles causing these stains can become mixed with the water in the pipes and result in red, rusty water at your faucets.
- Excessive iron may favor the growth of iron bacteria. These bacteria consume iron to survive and produce a red or brown slimy biofilm that can clog plumbing that leaves an unpleasant odor. These bacteria are naturally present in groundwater and shallow soils and can be introduced into a water system during construction or maintenance. There is no evidence that iron bacteria cause illness. They can, however, create an environment where other pathogens can flourish. They can also affect how much water a well produces.
- Iron-containing water, when used to make coffee, tea, or other beverages, can take on an unfavorable, harsh taste and an inky, black appearance.
- When used for cooking vegetables, the iron-containing water can make them dark and unappetizing.
- Excessive iron in water can also influence the level of other harmful substances like manganese.
How a water filter pitcher removes iron
Water filters can effectively remove excess iron from water using activated carbon or ion exchange resins.
Activated Carbon Filter
Activated carbon contains a very large surface area and very tiny pore spaces. These pore spaces can be as small as 2 nanometers or as large as 50 nanometers. The combination of tiny pores and large surface area provides the ideal conditions for iron to be adsorbed onto the filter.
Granular activated carbon (GAC) filters are especially effective at removing iron from water. However, all activated carbon filters can capture ferric iron via adsorption as the water flows through them.
Ion Exchange
Ion exchange can remove small quantities of ferrous iron from water. Ion exchange uses synthetic resins to exchange the undesired ions in the water for a pre-saturant ion in the solid phase. Sodium is typically used as an “adsorbent”.
The treatment involves running the water through an ion exchange resin media bed in the water filter pitcher. The iron and other ions are exchanged for sodium ions that are stored in the resin material temporarily.
Ion exchange is considered effective for water with less than 2-5 mg/L of dissolved iron.
Water Filter Pitchers That Remove Iron
Here’s a list of the best water filter pitchers that can remove iron from water. You can click on each to check their latest prices and availability.
1. Clearly Filtered Water Filter Pitcher

The Clearly Filtered Water Pitcher with Affinity® Filtration Technology is one of the best water filter pitchers that can remove 99.9% iron and other (>365) tap water contaminants.
This Clearly Filtered pitcher is tested for and meets NSF Standards to remove chlorine (NSF-42), up to 50 contaminants including VOC’s and heavy metals (NSF-53), herbicides and pesticides (NSF-401), microbes (NSF-244), and PFAS (NSF-P473).
This water filter pitcher features a three-stage filtration system with a woven mesh screen, granulated coconut carbon filtration layer for effective iron removal, and a composite shell of more than seven proprietary materials.
2. Epic Nano Water Filter Pitchers

Epic Nano water filter pitchers use US-made, high-quality water filters that are designed to remove up to 99.99% of contaminants, including iron (95.2%), bacteria, viruses, chlorine, fluoride, and lead.
These filters are certified by the National Sanitation Foundation and have been tested to remove chlorine (NSF-42), heavy metals (NSF-53), pharmaceuticals and pesticides (NSF-401), microbes (NSF-P231), and PFAS (NSF-P473).
3. Waterdrop Water Filter Pitcher

The Waterdrop water filter pitcher can effectively reduce water contaminants such as iron, VOCs, chlorine, mercury, heavy metals, and copper while retaining the beneficial substances. It comes with an advanced multi-stage filtration technology comprising coconut shell-activated carbon, ion exchange resin, and an activated carbon filter.
This NSF/ANSI 42 and 372 certified filter can purify 200 gallons of water and needs replacement every three months.
4. Crystal Quest Water Pitcher Filter

The Crystal Quest water filter pitcher employs a four-stage filtration system with an Eagle Redox Alloy® technology based on a high-purity copper-zinc formulation that removes 98% of iron via oxidation/reduction.
5. Epic Pure Water Filter Pitcher

The Epic Pure water filter pitchers are efficient iron (95.2%) reducing devices with a solid carbon block filter.
These US-made water pitchers are tested against 42, 53, 401, & P473 NSF/ANSI standards for filtering more than 200 contaminants, including chlorine, benzene, fluoride, mercury, lead, PFOAs, and microplastics.
6. Seychelle pH2O Alkaline Water Filter Pitcher
The Seychelle pH2O Alkaline Water Filter Pitcher is a great US-made device that can remove 95.41% iron from municipal water.
They are tested to NSF/ANSI standards 42 & 53 and can remove VOCs, toxic chemicals, PFOS, PFOA, trihalomethanes, aluminum, Heavy metals, asbestos, chromium 6, cadmium, copper, arsenic, lead, mercury, fluoride, and radon.
7. ProOne Water Filter Pitcher
The ProOne water filter pitcher relies on advanced gravity filtration technology to remove 99% of iron and other contaminants from water. This NSF/ANSI-42 certified pitcher can also remove chlorine, lead, heavy metals, microbes, VOCs, and chloramines.
8. Nakii Water Filter Pitcher
The Nakii water filter pitcher uses an innovative purification technology, activated carbon fiber (ACF), to efficiently remove excess iron, sulfates, mercury, chlorine, lead, and limescale. They are NSF/ANSI 42 and NSF/ANSI/CAN 372 certified for effective water filtration.
9. InvisiClean Water Filter Pitcher
The InvisiClean water pitcher has a 5-stage filtering system. Ion exchange and multi-layered carbon filters are the primary filters for reducing iron, mercury, barium, zinc, cadmium, arsenic, and lead, among other toxins.
10. ZeroWater Water Filter Pitcher
The ZeroWater water filter pitcher can remove 99.99% iron with its 5-stage water filtration system. This powerful filter pitcher is Certified to NSF/ANSI standards 42 and 53 and capable of removing PFOA/PFAS, lead and chromium, mineral, salts, and ions.
How do I know if my water contains iron?
Red or yellow-colored water usually indicates the presence of iron in the water. Red or brown particles settling at the bottom of the glass are also a strong indication.
The following information can help you determine what type of iron you have in your water supply and how best to treat it:
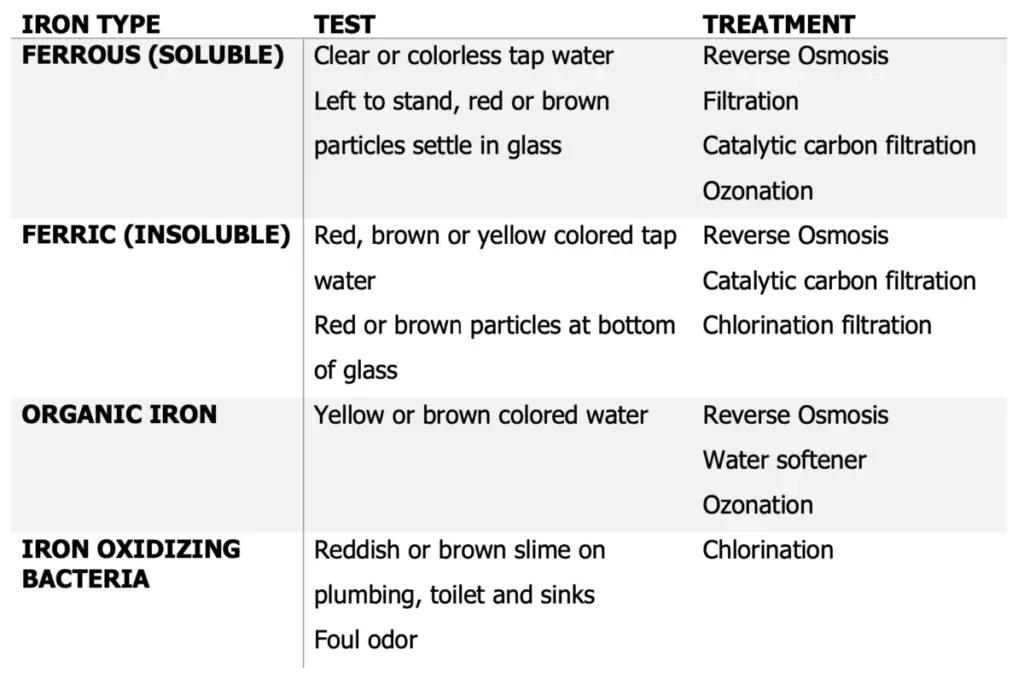
A laboratory can also provide you with a precise level of iron, which can help you choose the most appropriate course of action. My tap score has a specialized iron specific test available that can test your water with great accuracy including speciation (Ferric and Ferrous).
Is it Safe to Drink Water with Iron in it?
Drinking water containing iron (less than 0.3mg/L) poses no health risks to humans. In fact, iron helps to transport oxygen in the blood. Most tap water in the United States provides about 5% of the daily need for iron. Excessive iron in water, particularly ferrous iron, is not good for drinking as it gives water a metallic taste and undesirable color.
How Do you Know if you Have Too Much Iron in your Water?
Generally, excessive iron concentrations in water results in rusty color (red, brown or yellow), sediment, metallic taste, and orange or reddish staining on fittings and fixtures. When the pH of the water is below 6.5, it is more likely that iron will corrode from iron or steel pipes or other plumbing system components.
Finding the source of iron is the first step in determining whether the water supply has an iron problem.
Testing for iron concentration, iron bacteria, pH, alkalinity, and hardness should be the first steps in a laboratory examination of water to assess the degree of the iron problem and potential treatment options.






