PFAS is present in the blood of 97% of Americans according to a report released by the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). People are rightly concerned about poly-fluoroalkyl substances in their water and should remove them from their drinking water.
Under sink filters that use granular activated carbon (GAC), anion exchange resins (AER) or nanofiltration can effectively remove per- and poly-fluoralkyl substances (PFAS) from water. GAC and AER can remove up to 100% of PFAS, while nanofiltration is more than 90% effective.
This article will explain poly-fluoroalkyl substances, their types, potential health impacts, how under sink filters remove PFAS. We also discuss the best under sink filters available for removing PFAS.
What are per- and poly-fluoroalkyl substances?
Per- and poly-fluoroalkyl chemicals, also known as PFAS or PFCs, are substances used in making hundreds of products because of their non-stick properties. More than 9000 PFAS have been identified to date.
These man-made chemicals are used in making water, heat, stains, oil, and grease-resistant products, from clothing to food packaging, furniture, adhesives, electrical wire insulation, and non-stick and heat-resistant cookware.
PFAS is also used in the cosmetics, construction, and aerospace industries. Even in things like fake eyelashes.
The EPA established an acceptable level of PFOA and PFOS (the two main types of PFAS) in drinking water at no more than 70 parts per trillion (ppt) in a health advisory published in 2016. To give you an idea of how small 70 ppt is – it’s just 70 drops of PFAS in 1,000,000,000,000 drops of water.
Types of PFAS
There are numerous per- and poly-fluorinated chemicals (PFAS) – in fact there are more than 9000. Here are some of the more well-known PFAS that might be present in your drinking water.
- Perfluorobutane sulfonate (PFBS)
- Perfluorohexane Sulfonate
- Perfluorodecanoic acid (PFDA)
- Perfluorononanoic acid (PFNA)
- Perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA)
- Perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS)
- Perfluorobutyrate (PFBA)
- Polytetrafluoroethylene
- Perfluorohexanoic acid
Most Common PFAS Present in Water
The most common groundwater contaminants in the PFAS family are perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) and perfluoro octane sulfonate (PFOS). These have been the most extensively produced and are the most studied perfluorinated chemicals.
How PFAS Enter Our Water
PFAS are known as “forever chemicals” because they don’t break down and persist in the environment. They can travel from areas of environmental contamination to sources of drinking water.
They can even travel through soil seeping into groundwater sources. PFAS are found in lakes, rivers, and many types of land and water animals.
Health Impacts of PFAS
Exposure to PFOA and PFOS can lead to various health issues, including:
- Congenital disabilities
- Increase in cholesterol levels
- Changes in liver function
- Increase in high blood pressure
- Immune response abnormalities
- Pre-eclampsia in pregnant women
- Increased risk of obesity
- Increase in risk of cancer
- Fertility problems
- Thyroid problems
- Altered metabolism
- Reduced learning ability in kids
How Under Sink Water Filters Remove PFAS
Under sink filters with activated carbon, nanofilters, or ion exchange resins can effectively remove PFAS from water, particularly the most studied ones such as Perfluorooctanesulfonic acid (PFOS) and Perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA).
Granular Activated Carbon
Granular activated carbon (GAC) is activated carbon that is produced from organic sources with high carbon content, including lignite, coal, and wood. Activated carbon is a highly porous adsorbent material that provides a large surface area to which PFAS can adsorb.
According to EPA researcher Thomas Peth, GAC can be 100% effective for removing PFAS depending on the type of carbon, water flow rate, depth of carbon bed, type of PFAS, temperature, and other water contaminants.
This means that the more carbon there is, and the longer the water can remain in contact with the filter – the more successful the removal of the PFAS.
Under sink filters with granular activated carbon work more effectively against long-chain PFAS (such as PFOS and PFOA) than the short chain PFAS (such as PFBA and PFBS).
Granular activated carbon filters are also more effective at removing PFAS than carbon block filters.
Ion Exchange Resins
Ion exchange resins are composed of a polymeric, highly porous substance insoluble in water, acids, and bases. Hydrocarbons are used to create tiny beads of the resin. Ion exchange resins are predominantly of two types cationic or anionic.
Ion exchange resins draw in and hold contaminants as the water passes through them. The positively charged anion resins attract the negatively charged PFAS ions.
Anion exchange resins (AER) have been highly effective against PFAS, but it is more expensive than granular activated carbon.
Nanofiltration
Nanofiltration effectively removes 99% of PFAS concentrations on average, by membrane rejection and size exclusion processes while retaining the beneficial minerals found in water.
The membrane filtration process is best for use at home in the kitchen as often only a small volume of water needs to be treated.
NSF Certification
Filters that carry NSF/ANSI certification Protocol P473 indicate they have undergone testing to ensure that they can remove PFOS and PFOA from water.
To remove PFAS, a filter does not need to be NSF certified. It just demonstrates the consciousness of a brand to establish its reliability and authenticity among potential customers.
Best Under Sink Water Filters for Removing PFAS
The top 5 under-sink water filter systems for removing PFAS pollutants are listed below. You can click on each of them, and the link will direct you to the brand’s website or Amazon.com, where you can check their availability and price.
1. ClearlyFiltered 3-Stage Under the Sink Water Filter System
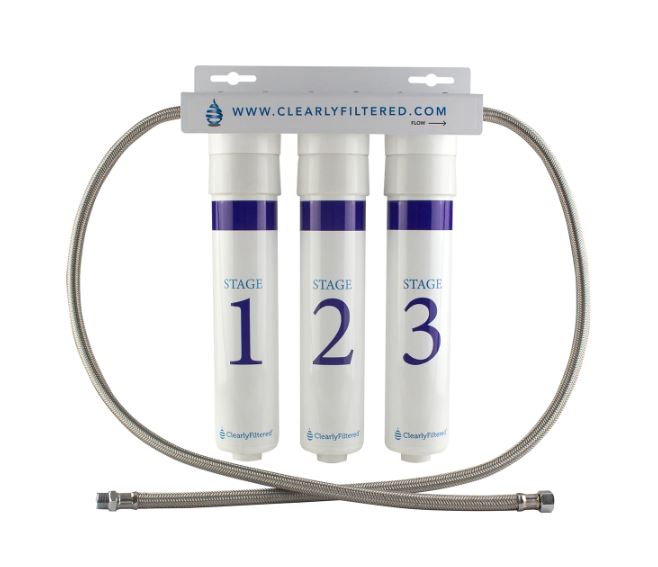

ClearlyFilterd features an advanced under-sink filtration system that can remove more than 99.6% of PFOA, PFDA, PFNA, and more than 99.8% of PFOS, PFBS, and Polytetrafluoroethylene.
This powerful filter combines activated carbon with their unique Affinity Filtration Technology to remove up to 99.9% of more than 232 water contaminants, including fluoride, lead, radiological elements, pharmaceutical drugs, herbicides, pesticides, semi-volatile compounds, phthalates, and VOCs.
Just connect it directly to your cold water line, and the system will start providing you with fresh and purified water immediately.
This model minimizes waste and is 75% more efficient than a typical reverse osmosis systems.
Remineralization is also not required, as it retains the healthier minerals found in water.
This under sink filter can purify 2000 gallons of water and needs to be replaced only once every 12 months.
Pros
- US-made
- Sleek and space-saving design
- Retains beneficial nutrients and minerals
- Long-lasting
- Easy DIY installation
- Easy to maintain
2. Epic Smart Shield Under Sink Filter
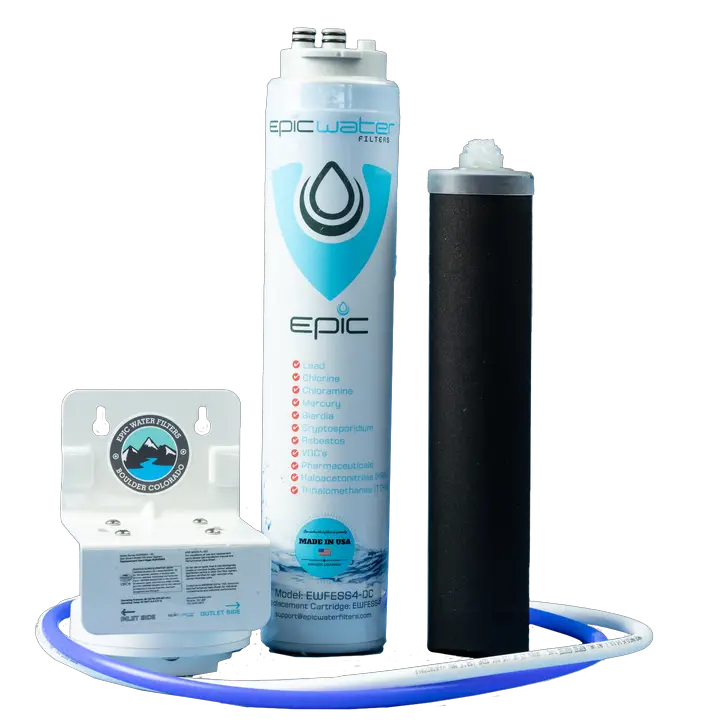

The Epic Smart Shield under sink filter comes with an activated carbon block filter for removing 98% of PFOS and 94% PFOA. Overall, this high-efficiency filter can remove 99.99% of more than 70 tap water contaminants.
The significant contaminants removed are lead, microplastics, glyphosate, chloramine, chlorine, industrial pollutants, and uranium.
With an average filter life of more than 12 months, it can produce up to 651 gallons of water.
Intelligent technology allows helpful minerals such as potassium, calcium, and magnesium to pass through the filter without being targeted.
Pros
- Us-manufactured
- Simple installation
- Hassle-free filter replacement
- Eco-friendly
- 100% recyclable
- 100% BPA free
- Alternative to more than 5000 landfill-bound plastic bottles
Water Purification Guide also has information on which water filters remove microplastics available here.
3. Crystal Quest SMART Under Sink Water Filter System
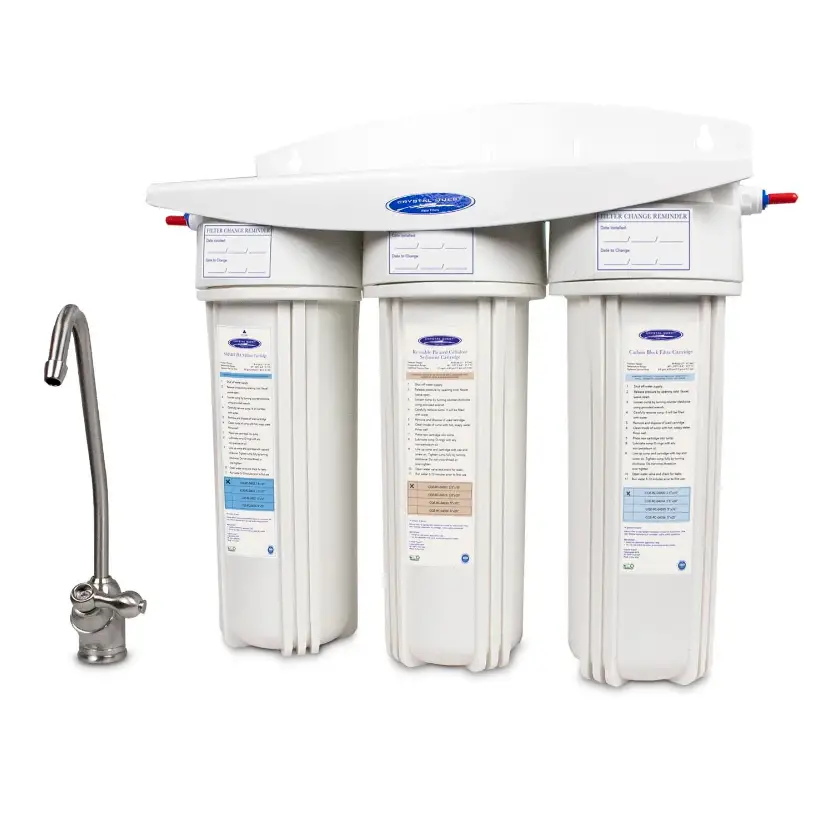

The Crystal Quest CQE-US-00309 smart under-sink water filter system can remove more than 85% of PFAS.
This model comes with a smart water filter cartridge containing a high-purity alloy blend of copper and zinc, ion exchange resin, carbon block, and granular activated carbon for efficient removal of chlorine, benzene, pesticides, insecticides, and herbicides, among others.
This filter system has a maximum flow rate of 0.5gpm (gallons per minute).
With a powerful filtration technology, this filter can clean 10,000 gallons of water and needs replacement only every 1-3 years, depending upon the quality of water.
Pros
- Attractive design
- Long-lasting
- High-efficiency water purification
- Easy to install and maintain
- A leak detector valve makes the water system flood-proof
4. Aquasana Claryum Under Sink Water Filter
The Aquasana AQ-5300 under-sink filter unit combines activated carbon, ion exchange, catalytic carbon, and submicron filtration to remove up to 96% PFAs, including PFOS and PFOA. The NSF certifications ensure that this filter can remove 77 impurities, chlorine, chloramines, and lead.
This model is upgraded with a new and improved design for a faster flow rate (44%). With up to 800 gallons of water, this filter can last six months longer than other products with the exact specifications.
This high-efficiency filter can remove water impurities while retaining the essential elements such as calcium, potassium, and magnesium so that you can enjoy a refreshing and epic taste of water.
Aquasana provides three faucet options with this filter system. You can choose from Brushed nickel, chrome, and oil-rubbed bronze finish faucets.
Pros
- Simple design
- NSF 42, 53, 401 and p473 certified
- Easy installation
- Easy filter replacement
Reverse Osmosis and PFAS
Another alternative to an in-line under sink filter is a reverse osmosis system that can also remove PFAS.
Water Purification Guide has a complete breakdown of reverse osmosis systems that remove PFAS here.
Does Boiling the Water Remove PFAS?
Boiling water does not remove PFAS. Instead, it can aggravate the situation by concentrating on the PFAS, thereby increasing the harmful effects.
What Water Filter will Remove all PFAS?
Granular activated carbon filters and anion exchange resins can remove 100% of PFAS. However, their efficiency depends on carbon type, choice of resin, bed depth, water flow rate, types of PFAS, variety of organic matter, and chemical contaminants present in water.

