Drinking water contaminated with heavy metals poses serious health risks, and it is essential to purify water using point-of-use water filtration systems such as water filter pitchers.
Water filter pitchers with nanofiltration, activated carbon, or ion exchange resins can effectively remove various heavy metals from water. Some water filter pitchers use a combination of these methods to remove greater than 98% of heavy metals, including arsenic, lead, zinc and copper.
This article will explain heavy metals, their negative impacts, symptoms of exposure to heavy metals, water filters for removing heavy metals, and a list of the best water filter pitchers for removing heavy metals. We’ll also address some frequently asked questions regarding heavy metals and where to buy a Heavy Metals water testing kit.
What are Heavy Metals?
Heavy metals are naturally occurring metallic chemical elements that have a high density and atomic weight.
Their widespread distribution in the environment as a result of their numerous industrial, residential, medical, agricultural, and technical applications has raised concerns however about their potential effects on the environment and our health.
Some of the more common heavy metals are:
- Lead
- Arsenic
- Cobalt
- Copper
- Cadmium
- Selenium
- Chromium
- Zinc
- Nickel
Lead, cadmium, arsenic, mercury, and chromium are hazardous to human health and the environment. Lead and zinc can also cause corrosion and have been cause for particular concern across the U.S. because of their use in water lines.
If you are looking for water filters that can remove aluminum, Water Purification Guide has information available here.
Factors Affecting Toxicity of Heavy Metals
The toxicity of heavy metals depends upon the following factors:
- Dosage
- Route of exposure
- Chemical species
- Gender
- Age
- Genetics
How a Water Filter Pitcher Removes Heavy Metals
Water filter pitchers with nanofiltration, carbon filtration, or ion exchange can effectively remove heavy metals from water (unless at excessive concentrations – such as those related to an industrial accident or spill).
Nanofiltration
A nano filter has a small pore size between 0.0002 and 0.002 microns, falling between ultrafiltration and reverse osmosis. When water containing heavy metals passes through the nano filter, it traps the heavy metal particles leaving the water purified.
A study (ref 1) reported a high rejection percentage of heavy metals using nanofiltration with 99.7% for chromium, 98.4% for copper, 97.2% for nickel, and 97.9% for zinc.
Carbon Filtration
Activated carbon filters remove contaminants from water by the process of adsorption. Adsorption is one of the most cost-effective and efficient ways of removing heavy metals from water. Activated carbon acts like a sponge to adsorb the heavy metal molecules leaving the water clean.
The metals adsorb onto the surface of the carbon and remain there, accumulating until the carbon filter is replaced.
This is an eco-friendly technique that provides excellent flexibility in design and operation.
Ion Exchange
Ion exchange processes are becoming highly popular in removing heavy metals from water.
Ion exchange can remove common water contaminants such as arsenic, mercury, chromium, zinc, lead, copper, and nickel.
NSF Certification
The National Sanitation Foundation (NSF) is a non-profit international organization that develops performance criteria for water treatment systems. Consumers should assess the pitcher’s test results to determine whether claims about effectiveness are reasonable because companies can unfortunately make unsupported claims about their products.
The NSF listing mark is displayed on items and in product advertising materials if they have undergone NSF testing and satisfy their minimum requirements.
There are numerous NSF certifications, each relating to a different contaminant or filtration system.
NSF 53
The NSF 53 standard specifies the minimum requirements for systems that intend to decrease particular contaminants that are harmful to human health, including heavy metals like lead, copper, chromium, cadmium, etc.
Ideally, a water filter pitcher will have been tested against NSF53 criteria to demonstrate it can effectively remove heavy metals – However, NSF certification is not mandatory and is simply desirable!
Common Heavy Metals and their Removal Rate by the Leading Brands of Water Filter Pitchers
Here’s a list of the common heavy metals found in water and their removal percentage by different water filter pitchers arranged (left to right) according to the ASTDR’s substance priority list. More detail is provided on each of these filters below.
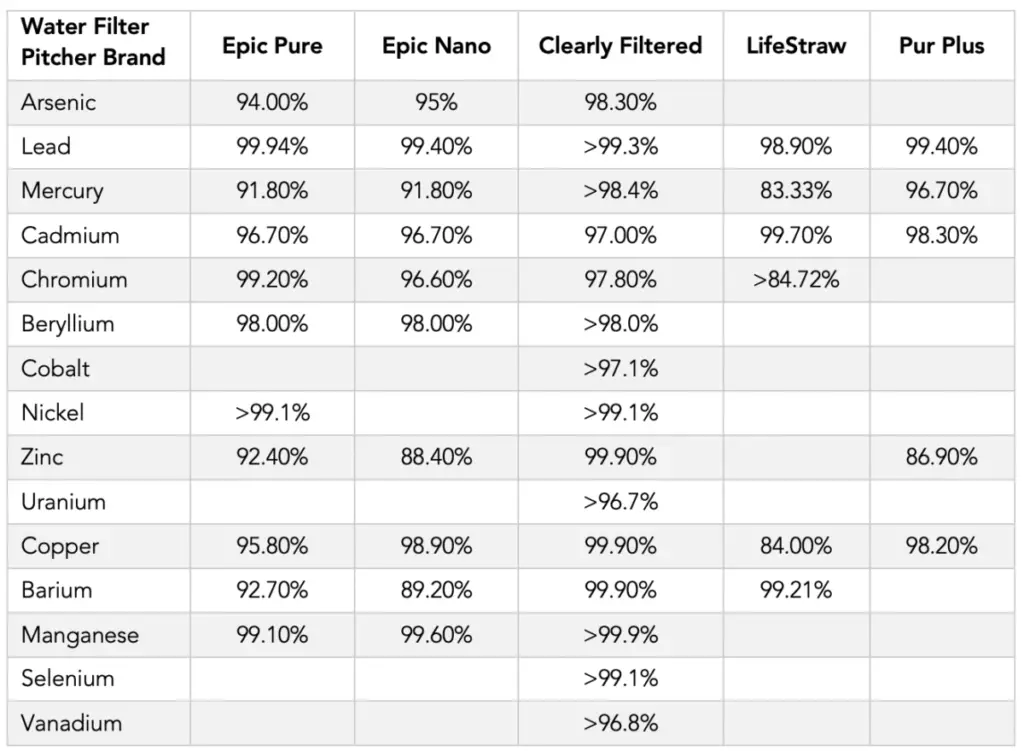
Water Purification Guide has more information on how to test for contaminants in your water available here.
Best Water Filter Pitchers That Remove Heavy Metals from Water
There are several water filter pitchers that can effectively remove heavy metals from water. Here’s the list of the best water filter pitchers that can remove heavy metals from your drinking water. You can click on each name to check the availability and latest prices on amazon or their respective website.
1. ClearlyFiltered Water Filter Pitcher

The Clearly Filtered features one of the most effective water filtration systems capable of removing a wide range of heavy metals from water. With Affinity® Filtration Technology, these filter pitchers can remove up to 99.9% of more than 365 water contaminants.
These high-quality filters are independently tested against NSF 42, 53, 244, 401, and 473 standards. Intelligent technology allows the beneficial minerals to pass through the filter, retaining them in drinking water.
The filter needs replacement every four months with an average filter life of 100 gallons. The 80 oz capacity of the pitcher would be more than enough to keep you hydrated the whole day.
The highest heavy metal filtration capacity outweighs this filter pitcher over others on our list.
Pros
- US-manufactured
- Large capacity
- Long-lasting
- 100% BPA/BPS free
- Built-in water dam to prevent spillage
- Large solid grip handle
- Lifetime warranty
2. Epic Pure Water Filter Pitcher

The Epic Pure water filter pitcher features a solid carbon block design for the efficient removal of heavy metals along with 99.9% of other tap water contaminants.
These American-made filters are tested against NSF/ANSI standards 42, 53, 401, and P473. Each filter can purify 150 gallons of water, making it an ideal economical choice. This is also eco-friendly as it saves 1000+ single-use plastic bottles from going into landfills.
This high-quality water filter pitcher comes with a 51 oz upper reservoir and 68 oz lower reservoir, eliminating the need to buy filtered water.
With normal use, the filter needs to be replaced every three to four months.
Pros
- US-made
- 100% recyclable and replaceable
- Long life span
- Tested in multiple labs to remove more than 200 contaminants
- BPA free
- LED timer for filter life countdown
- Lifetime warranty
3. Epic Nano Filter Water Pitcher

The Epic Nano water filter has a submicron filter for removing heavy metals and 99.99% of other water contaminants, including microbes.
These filters are independently tested in different labs to remove more than 200 contaminants from water. They are also tested to NSF/ANSI Standards 42, 53, 401, P473, and P231.
The filters can purify 150 gallons of water and need to be replaced every three to four months on average.
You can add 51 oz of water to the upper reservoir, while the bottom reservoir can hold 68 oz of purified water. With a fast flow rate, this pitcher can purify the water to its maximum capacity within 10 to 15 minutes.
Pros
- US-made
- Extensive capacity
- Lasts longer
- Recyclable
- Substitute of up to 1500 plastic bottles
- BPA free
- Filter life countdown timer
4. LifeStraw Home Water Pitcher
The LifeStraw water filter pitcher comes with a membrane microfilter, ion exchange, and a carbon filter to efficiently remove heavy metals from water. Besides heavy metals, these filters can also remove more than 30 contaminants, including PFOS, parasites, and microbes, from the water, making it safe to drink for you and your family.
These robust filters are certified to NSF standards 42, 53, 401, P231, and P473. Besides the removal of harmful water contaminants, these filters are capable of retaining essential minerals such as magnesium and potassium.
The membrane microfilter can last up to 246 gallons of water, while the ion exchange and carbon filter 40 gallons of water need to be replaced every two months.
These water filter pitchers are available in 7 (56 oz) and 10 (80) cup sizes, perfect for a whole family.
Pros
- Large capacity
- Durable
- BPA-free food-grade material
- Easy-fill lid
- Easy to set up and use
- Three years warranty
5. Pur Plus Water Filter Pitcher
The PUR Plus water filter can efficiently remove common heavy metals found in water. The PUR plus filter includes a granulated activated carbon, ion exchange resin, and advanced pleated paper for removing various water contaminants.
These water filters are WQA certified to reduce lead and other harmful contaminants from water.
Each new water filter provides 40 gallons of filtered water for up to two months of regular use. This water filter pitcher provides 7 cups (56 oz) of water. PUR also features other water filter pitchers varying from 7-12 cups.
With a slim design, these water filter pitchers are pretty space efficient. With great-tasting clean water, this pitcher saves many plastic bottles from going into landfills.
Pros
- Filter change indicator light
- Easy fill tight lid
- Dishwasher safe
- BPA free
Other Methods of Removing Heavy Metals from Water
Reverse osmosis and distillation are other efficient methods for removing heavy metals from water.
Reverse Osmosis
Reverse osmosis works by pressurizing water to pass through a semipermeable membrane. To produce clean drinking water, water flows from the more concentrated (with more contaminants) side of the RO membrane to the less concentrated one (having fewer contaminants).
According to a research report, the removal rate of different heavy metals from water using reverse osmosis was 99.3% for copper, 99.9% for chromium, 99.5% for zinc, and 99.5% for nickel.
Reverse osmosis systems are often combined with a portable pitcher so that you can enjoy pure and clean water on the go.
Water Purification Guide has more information on how reverse osmosis removes lead from water available here.
Distillation
The distillation process involves heating the tap water to boiling and cooling it immediately. The system generates steam, which rises and leaves contaminants behind. The steam then passes through condensing coils, which cools and become liquid again. The distilled water is then deposited in a storage container. Distillers create nearly pure water free of heavy metals, minerals, and salts, resulting in a bland taste.
Distillation removes total dissolved solids (TDS) of water, including almost all heavy metals such as arsenic, lead, cadmium, and copper.
Distillers range from small-sized units that distil less than one quart of water per hour to large-sized rectangular carts that produce about one and a half gallons of water per hour. Distillation devices are often installed as point-of-use units at the faucet rather than being used to treat all the water entering the house because they only produce a small volume of treated water.
FAQ
How do Heavy Metals Enter our water?
Heavy metals can contaminate both our surface water and groundwater. These contaminants can localize and remain in the soil through precipitation or ion exchange. Unlike organic pollutants, heavy metals do not decompose and present a unique set of challenges for remediation.
According to the EPA, heavy metals typically seep into our drinking water supply from:
- Household plumbing
- Mining operations
- Electronic manufacturers
- Natural mineral deposits
- Cement plants
- Petroleum refineries
- Municipal waste disposal
Negative Impacts of Heavy Metals on the Environment
Heavy metals can also cause corrosion, acid rain formation, deterioration of infrastructure, and eutrophication.
What are the Health Impacts of Heavy Metals?
Heavy metals typically bioaccumulate in the body. Bioaccumulation occurs when an organism absorbs a chemical more quickly than it is excreted from the body.
Excessive exposure to heavy metals can disrupt the body’s normal functions and lead to heavy metal poisoning. Drinking water contaminated with heavy metals can cause both acute and chronic poisoning. Heavy metals that can be hazardous include lead, mercury, arsenic, cadmium, and chromium.
According to the WHO, various heavy metals affect the body differently.
Lead
Exposure to lead can elevate blood pressure in adults, while in children, infants and fetuses, it affects the neurobehavioral and developmental processes.
Cadmium
Cadmium can damage bones and kidneys. It is a potential human carcinogen mainly known for causing lung cancer.
Mercury
Mercury is highly toxic and can damage the liver, kidneys, immune system, and nervous system.
Arsenic
Arsenic-contaminated water increases the risk of skin cancer, pigmentation, and skin lesions.
Chromium
Oral exposure to chromium can lead to hematological toxicity, DNA damage, gene mutation, and carcinogenicity.
Heavy metals negatively impact cellular events of the body, including growth, differentiation, apoptosis, proliferation, and repairing.
Symptoms of Exposure to heavy Metals
There are series of symptoms associated with both acute (short-term) and chronic (long-term) exposure to heavy metals. Several of these symptoms are specific to a particular metal, however there are some common ones that can be experienced from exposure to most (if not all) of these metals):
Acute Exposure
- Abdominal pain
- Diarrhea
- Headaches
- Nausea
- Vomiting
Chronic Exposure
- Cardiovascular disease
- Increased risk of cancer
- Damage to body organs
- Skin lesions
What Happens if I Drink Water with Heavy Metals in it?
Drinking water contaminated with heavy metals causes toxic metals to bioaccumulate in the body over time. Heavy metal bioaccumulation raises the risk of developing cancer and other diseases. Drinking water with a high concentration of heavy metals is linked with renal injuries, neuronal damage and cardiovascular disorders.
Heavy metals should be removed from water prior to consumption, activated carbon filtration, reverse osmosis, distillation and nanofiltration are effective means of removing the heavy metals in water making it safe to drink.
Do Brita Water Filters Remove Heavy Metals?
The performance data of Brita filters shows that some filters can effectively remove heavy metals from water. The Brita Elite and LongLast filters have the best heavy metal removal efficiency rates. However, the Brita bottle and Stream filters do not remove heavy metals.
- The Brita Elite™ filter can remove 99.2% of cadmium, 99.6 % of lead, and 95.9% of mercury.
- The Brita Standard filters can reduce copper (94%), mercury (96%), cadmium (96%), and zinc (64%)
- Brita Long Last filters can remove lead (99.5%), mercury (95.5%), and cadmium (99.2%).
- Brita Longlast+ filters can remove lead (99.6%), mercury (95.9%), and cadmium (96.9%).
- Brita faucet filters can remove more than 99.3% of lead.
- Brita Bottle and Stream filters don’t remove any of the heavy metals.
How do I know if my Water has Heavy Metals in it?
To detect the presence of heavy metals in your water, a sample should be collected and tested at a certified lab near you.
Tap score (operated by Simple Labs) provides one of the best water testing services for heavy metals (Home Water Test: Essential) that can test for 23 different heavy metals in your water. Tap score water tests are available across the U.S. and provide compliance-ready resources.
- Order today and they’ll send out the kit and instructions on how to collect the samples.
- Shipping is included both ways.
- Samples are tested in a certified laboratory.
- With a 5-day turnaround, you’ll get a detailed test report for about 54 analytes along with recommendations on possible treatment options.
For more information and to order your Home Water testing kit (Essential) click here.
Does Tap Water have Heavy Metals?
Significant amounts of heavy metals may be found in tap water. The EPA sets maximum legal limits for contaminants in tap water to safeguard human health. However, the leaching of heavy metals from domestic plumbing or service lines can contaminate tap water after the water is purified and tested.
The drinking water that is usually sourced from domestic wells or groundwater systems might contain elevated concentrations of heavy metal contaminants from mining operations, municipal waste disposal sites, or naturally occurring mineral deposits. This way, the water reaching your home is usually contaminated with arsenic, cadmium, lead, copper, chromium, selenium, and other impurities.
References:
1. Al-Alawy, A.F. and Salih, M.H., 2017. Theoretical and experimental study of nanofiltration and reverse osmosis membranes for removal of heavy metals from wastewater. Int. J. Sci. Res.(IJSR), 6, pp.778-788. <DOI:10.21275/art20178885>



